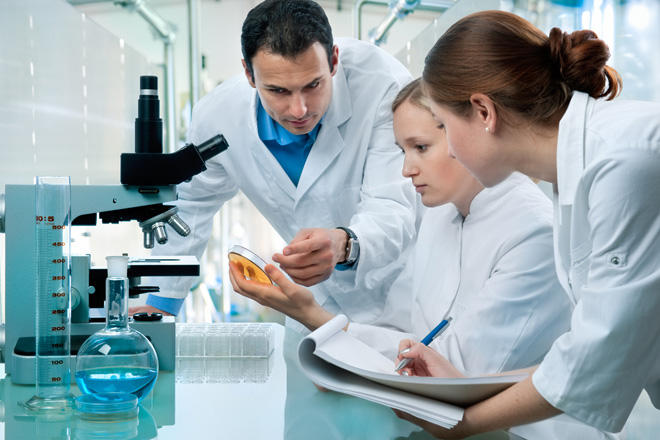
The study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is based on the chemical methylation process, an enzymatic reaction during which a methyl group CH3 is added onto DNA or proteins.
The identification of cellular pathways controlled by methylation and by the enzymes that add the methyl group is important to understanding basic processes in human cells and deciphering the mechanisms of disease development such as cancer and diabetes.
Uncontrolled division of cells is a major factor in the development of cancerous tumors, and the study showed that methylation is involved in determining the pace of cell division progression.
The study found that the methylation of PLK1, a key protein in controlling cell division, by the SETD6 enzyme regulates the cells division's pace.
According to the study, without methylation the PLK1 protein shows increased activity leading to faster cell division, resulting in faster cell proliferation.
The team is also working on the development of SETD6-specific inhibitors, to be used in the future to develop alternative treatment strategies for various diseases.
Xinhua
More about: