China bird flu deaths surge in what could be the worst season ever

Authorities have repeatedly warned the public to stay alert for the virus, and cautioned against panic in the world`s second-largest economy.
But the latest bird flu data has sparked concerns of a repeat of previous health crises, like the 2002 outbreak of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).
"It`s mid-February already and we are just getting the January numbers. With the death rate almost catching up with SARS, shouldn`t warnings be issued earlier?" said one user of popular microblog Sina Weibo.
Other netizens in the Chinese blogosphere worried about the pace of infections, and called for even more up-to-date reports.
China has come a long way in learning how to communicate to the public and to respond to health crises since the SARS outbreak, when official reports of infections were criticized for their slowness and irregularity.
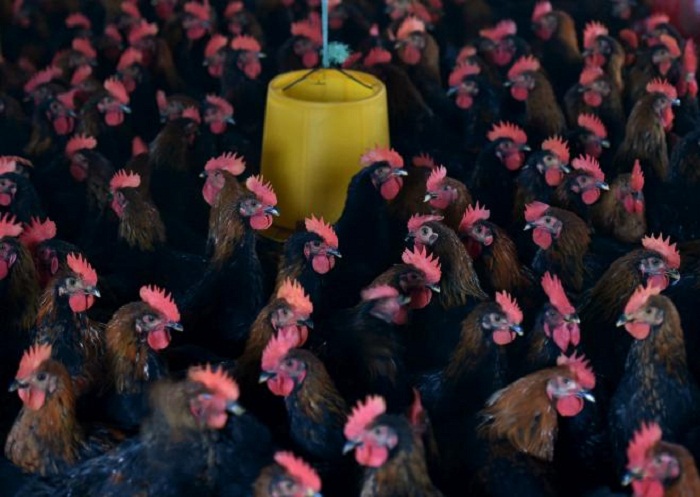
The People`s Daily, the official paper of the ruling Communist Party, warned people in a social media post to stay away from live poultry markets, saying it was "extremely clear" that poultry and their excrement were the cause of the infections.
Chinese chicken prices sank to their lowest levels in more than a decade on Wednesday, hammering meat processors` share prices amid fears that bird flu could hit demand in one of the world`s top poultry markets.
RECORD HIGH INFECTIONS
China, which first reported a human infection from the virus in March 2013, has seen a sharp rise in H7N9 cases since December. The official government total is 306 since October, with 192 reported last month.
But others estimate a higher number of infections.
The Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota last week estimated China had at least 347 human infections so far this winter, eclipsing the record of 319 seen three years ago.
On a week-to-week basis, it was difficult to tell if H7N9 cases were still rising in China or have peaked, CIDRAP said in a report on its website on Feb. 10.
Some provincial health departments in China announce individual cases as they are confirmed, while others wait to include them in their monthly updates.
"An important factor in the past waves of H7N9 cases among humans in China has been rapid closure of live poultry markets," said Ian Mackay, a virologist at the University of Queensland in Australia.
"This season there seems to have been a slower response to the outbreak, which may be leading to greater numbers of human exposures to infected birds."
The National Health and Family Planning Commission has yet to respond to a request from Reuters seeking comment on the recent bird flu deaths.
Most of the H7N9 human infections reported this season have been in the south and along the coast.
Beijing on Saturday reported its first human H7N9 case this year. The patient is a 68-year-old man from Langfang city in neighboring Hebei province.
A second human case was reported on Tuesday.
/Reuters/