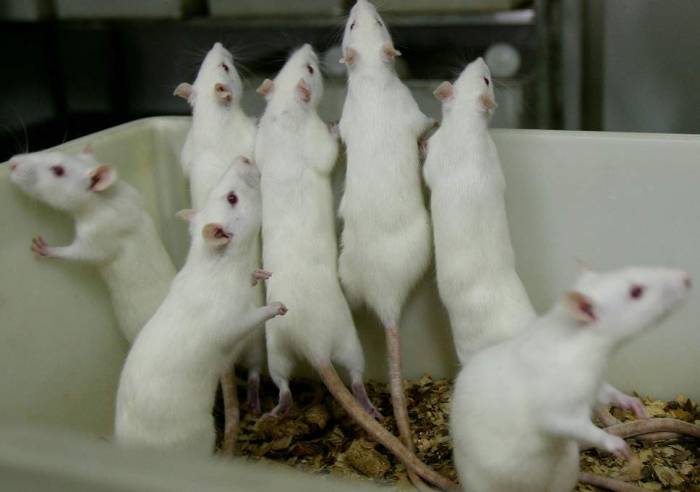
The rats regained the ability to use their paws and were able to pick up sugar cubes to feed themselves after scientists at King’s College London used gene therapy to repair damage to their spinal cords.
“In some of the tests we looked at – such as gripping the rungs of a ladder – the treatment worked within one to two weeks,” Professor Elizabeth Bradbury, who led the study, told Sky News. "Other tests, such as picking up objects, needed very skilled muscle function. They need to be able to reach, grip, turn the wrist and lift it back.
“Those took a much longer period of time – we started seeing recovery in five to six weeks.”
The rats had been given injuries to their spinal cords which mimic those humans typically suffer in car accidents or falls.
They were then given an injection to the spinal cord which contained a gene that makes an enzyme called chondroitinase
The enzyme breaks down scar tissue which forms after damage to the spinal cord, stopping new connections from forming between nerves.
Once the tissue is broken down, the nerves can grow again, form new connections and restore muscle movement.
“The rats were able to accurately reach and grasp sugar pellets,” Dr Emily Burnside, one of the researchers, told the BBC in a separate interview. “We also found a dramatic increase in activity in the spinal cord of the rats, suggesting that new connections had been made in the networks of nerve cells.”
Professor Bradbury told the broadcaster: ”We find this really exciting, recovery of this type of function, because for spinal injured patients their highest priority is to get their hand function back.
“Being able to pick up a coffee cup, hold a toothbrush, these types of things will have a dramatic increase on their quality of life and their independence.”
The Independent
More about: gene