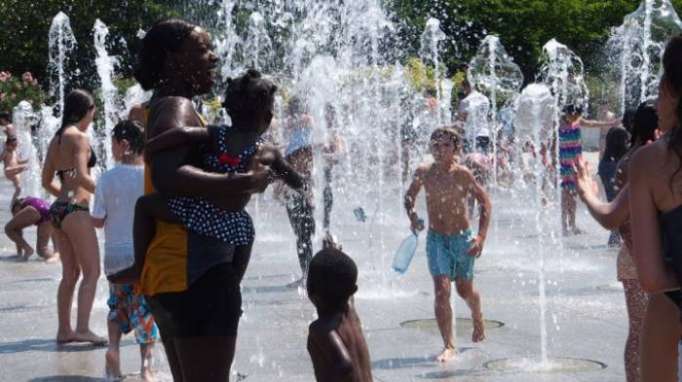Dehydration, when the body doesn’t have enough water is one risk; overheating is another – it can make symptoms worse for people with chronic heart or lung problems; heat exhaustion; and finally heat stroke.
The health effects of hot weather are linked to the body’s ability to adapt to heat by acting as a natural cooling system. The main ways in which the human body eliminates heat during thermal stress are through sweat production, increased cardiac output and redirection of blood flow to the skin. These responses can be diminished or delayed in older people or other susceptible groups such as those with chronic illness or people taking certain drugs. Young children are also more susceptible to the negative effects of prolonged heat.
Are there particular diseases that cause additional problems during a heatwave?
If you have had a heart attack, a stroke or suffer with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, extra caution is needed. High levels of air pollution, coupled with warm weather, have been shown to increase the number of strokes by 50 per cent. Asthma sufferers are vulnerable to high pollen counts. And people with diabetes, neurological disorders and psychological illnesses may also be at increased risk.
Those taking drugs such as diuretics which are designed to get rid of body fluids may benefit from a reduced dose during a heatwave. Seek medical advice first.
What should you look out for in someone who is overheating dangerously?
Excessive thirst, nausea, vomiting and muscle cramps are signs of heat exhaustion. Untreated, it progresses to heatstroke: watch out for heavy sweating that suddenly stops; a rapid heart rate and rapid breathing; and neurological symptoms such as confusion and a loss of co-ordination. Heatstroke is a medical emergency that requires urgent medical attention.
Irish Times
More about: