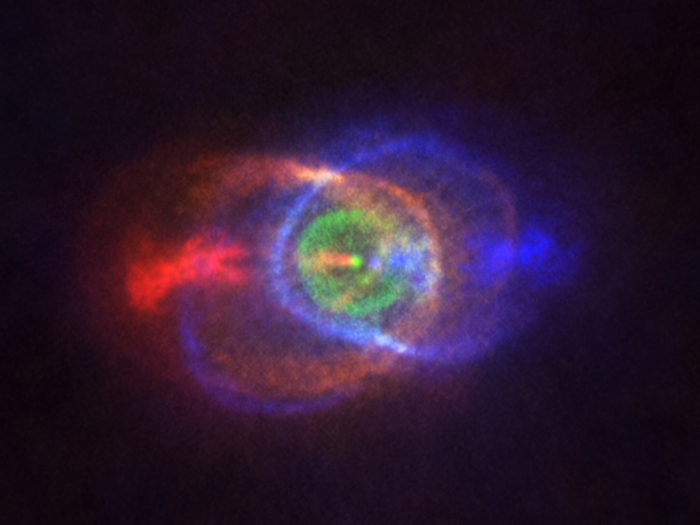
Astronomers have released a stunning image of the celestial cloud left in the wake of a fight between two stars.
The unusual cloud can be seen in images taken from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, 66 telescopes that together make the biggest astronomical project on Earth.
They show the aftermath of a collision that saw one star grow so big it swallowed the other, which then fell towards its partner and made it shed its outer layers.
It created an unusual object that scientists hope can teach them about the way stars are formed anddie.
"The star system HD101584 is special in the sense that this 'death process' was terminated prematurely and dramatically as a nearby low-mass companion star was engulfed by the giant," said Hans Olofsson of the Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, who led a recent study, published in Astronomy & Astrophysics, of this intriguing object.
By looking at data taken from ALMA and other experiments, scientists were able to recreate the fight that left the double-star system in such a beautiful mess.
It happened when the main star started to die, and in doing so grew into a red giant, getting so large it could engulf the other. The smaller star then spiralled towards the core of the bigger one, but they stayed apart.
Rather than leading to a direct collision, the two's movements around each other made the bigger star burst, throwing its gas layers across the cosmos and leaving it with an exposed core.
The structure of the nebula that can be seen in the image came about as the smaller star spiralled towards the bigger one, and the jets of gas that formed as it did. Those jets then shot through the material that had been thrown out, and helped formed the post-fight detritus that can be seen spread across the universe.
The fight could help prefigure what will happen to other stars – including our own Sun.
"Currently, we can describe the death processes common to many Sun-like stars, but we cannot explain why or exactly how they happen," said co-author Sofia Ramstedt from Uppsala University, Sweden, in a statement.
"HD101584 gives us important clues to solve this puzzle since it is currently in a short transitional phase between better studied evolutionary stages. With detailed images of the environment of HD101584 we can make the connection between the giant star it was before, and the stellar remnant it will soon become."
The Independent
More about: gascloud